Types of Studies, Controls, Demand Characteristics
1/10/22
Types of Studies (continued from last week)
In general, it is helpful to classify studies according to four criteria:
- Does the researcher simply describe and observe? Or does the researcher offer an interpretation or explanation? (That is, does the study offer an explanatory theory?)
- Does the researcher make a prediction? (That is, does the method invite failure?)
- Does the researcher manipulate the world? (That is, does the method allow the researcher to infer causality?) And
- Does the researcher count or measure something? (That is, is the research qualitative or quantitative?)
A Table
| Explanatory Theory | Hypothesis Tested | Infer Causality | Quantitative | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reconnaisance | ||||
| Descriptive | post hoc | |||
| Measurement | ✓ | |||
| Correlational | a priori | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Exploratory Correlational | post hoc | ✓ | ||
| Exploratory Experimental | post hoc | ✓ | ✓ | |
| (True) Experimental | a priori | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Meta-Study | a priori | (✓) | (✓) | ✓ |
Measurement Studies
The measurement study is a type of exploratory study.
It differs from the reconnaissance and descriptive studies insofar as some sort of measurement is involved.
It differs from the exploratory correlational study insofar as the researcher doesn’t attempt to determine whether there are relationships between any of the measurements.
Measuring Syncopation
In order to measure syncopation, we had to make an operational definition. In metrically organized music, each moment can be regarded as occupying a particular point in the metric hierarchy. The highest point (labelled “1”) might be defined as coinciding with the downbeat. The second highest point (“2”) coincides with the third beat in 4/4 meter. Other points in the metric hierarchy can be similarly labelled as shown in Figure 1.
See this Huron and Ommen study: (emp_methods_workshop)
Correlational Study
Correlational studies aim to identify linkages or relationships between things. We say two things are correlated when there is some sort of connection or association between them.
For example, music with a fast tempo tends to be louder than music with a slow tempo. Although there are exceptions to this, in general, there is a correlation between tempo and dynamic level.
Correlational Study
- Correlational studies may or may not be hypothesis-driven. When there is no a priori hypothesis, the study is said to be an exploratory correlational study.
- Correlational studies always involve at least two sets of measurements.
- A common type of correlational study is the survey or questionnaire.
Experimental Study
- What distinguishes an experiment from all other kinds of studies is that the experimenter manipulates the world. Rather than being just a passive observer, the experimenter intentionally makes some change and then observes the effect of the change.
Experimental Study
- The variable manipulated by the experimenter is called the independent variable (or independent measure). The variable observed by the experimenter is called the dependent variable (or dependent measure).
Exploratory Experiment
An Exploratory Experiment involves manipulation and measurement, but the manipulation is not motivated by some prior theory, hypothesis or conjecture.
- For example, a researcher might play traditional Japanese and Andean pop music to naive Western listeners while making a series of measurements, such as heart-rate, respiration, body temperature, and observable behavior, etc. The researcher may have no idea what to expect. That is, no prediction was made.
Meta-Study
A meta-study is a “study of studies.”
- It is typically done when a large number of studies have been carried out related to some problem.
Modeling Study
- Theories can often be implemented as models. An example of a physical model is a large model of San Francisco Bay built by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (see photo).
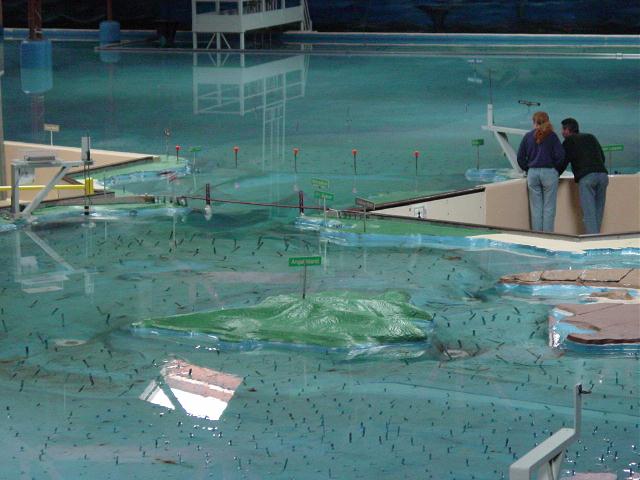

SF Bay
Pilot Study
- A pilot study is carried out simply as a way of testing the research procedure. Pilot studies usually involve relatively small numbers of participants or small sample sizes.
Mixed Methods
The research might begin by reporting a descriptive study. The results from the descripive study may inspire the authors to formulate a theory, from which a hypothesis is generated. The article might then go on to report a correlational study or an experiment whose purpose is to explicitly test the hypothesis.
Natural Experiments
A special kind of experiment is the so-called natural experiment. A natural experiment relies on a manipulation of the real world that occurs without the intervention of the researcher.
In March of 2020, climate scientists studied the lessening of air pollution during lockdown.
There is a manipulation being made of sorts and a control condition, but it really is only possible at a grand scale because of an uncontrollable global event.
Clever Hans
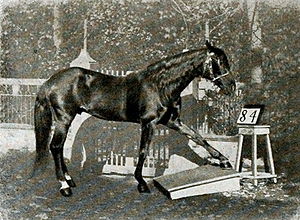
Clever Hans
Clever Hans

Clever Hans
Clever Hans
[From Wikipedia:] “Hans was a horse owned by Wilhelm von Osten, who was a mathematics teacher, an amateur horse trainer, phrenologist, and something of a mystic. Hans was said to have been taught to add, subtract, multiply, divide, work with fractions, tell time, keep track of the calendar, differentiate musical tones, and read, spell, and understand German. Von Osten would ask Hans,”If the eighth day of the month comes on a Tuesday, what is the date of the following Friday?” Hans would answer by tapping his hoof. Questions could be asked both orally, and in written form. Von Osten exhibited Hans throughout Germany, and never charged admission.”
Clever Hans
Clever Hans Effect: An experimenter may inadvertently provide non-verbal (or verbal) cues as to what they hope will happen. People can be even more tuned-in than a horse in reading body language.
Demand Characteristics
- Demand Characteristics: when an experiment becomes invalid because of what participants believe is the purpose of the experiment, right or wrong
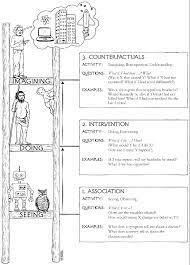
Pearl’s Ladder of Causality
Confounding
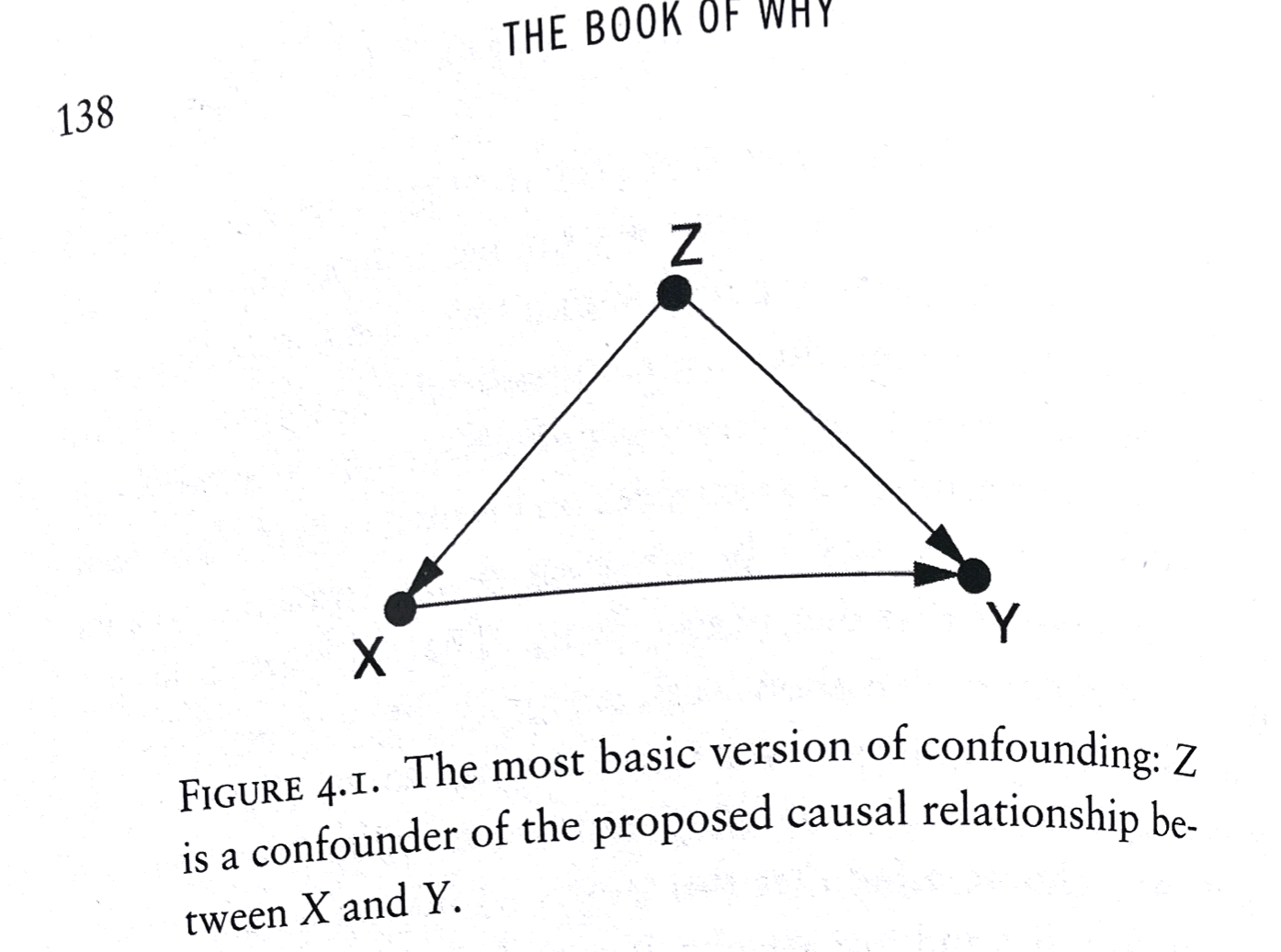
Controls
Confounding
Confounding
Third Variables
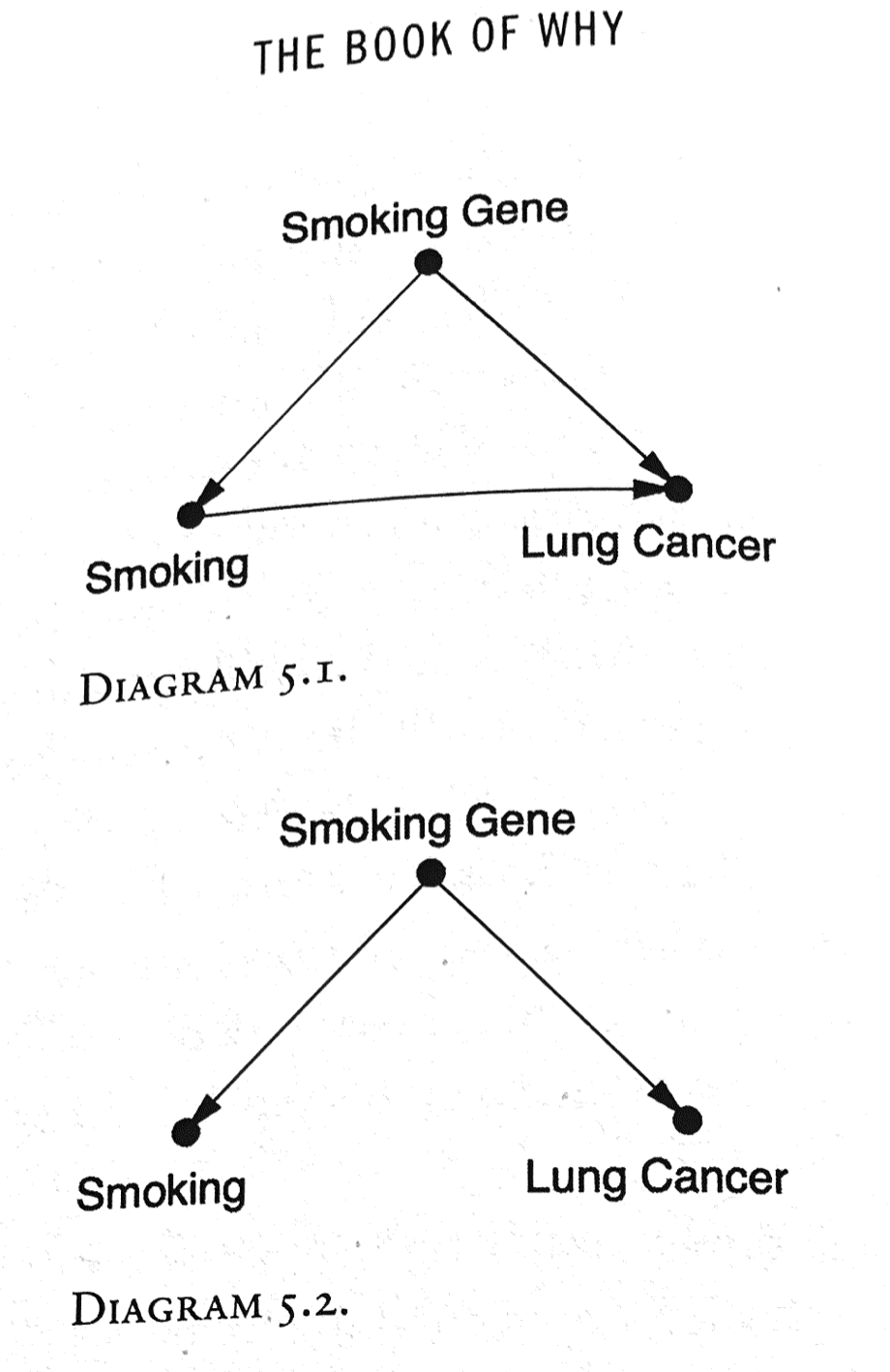
Smoking
Front Door and Causality
p(cancer|smoking)